Largely neglected and generally undervalued, ponds are actually remarkably important for biodiversity conservation. The EU-funded PONDERFUL project investigates how ponds can be used as nature-based solutions (NBS) for climate change adaptation.
LEARN MOREThe significance of ponds has long been underestimated and they lie largely outside regulatory systems. However, thanks to their abundance, heterogeneity, exceptional biodiversity inherent naturalness and biogeochemical potency, ponds play a crucial role in catchments, landscapes, and potentially at continental scale which is completely out of proportion to their small size.
The overarching aim of the project, led by the University of Vic (Spain), is to develop improved methods for maximising the use of ponds and pondscapes to mitigate and adapt to climate change, protect biodiversity and the delivery of ecosystem services.


30-50% of standing water worldwide
70% of regional freshwater species pool in European landscapes, many of them rare, endemic or threatened species
50-90% of of pond losses in European countries over the past century
Significant role in mitigating and adapting to climate change
Ponds deliver multiple ecosystem services and NPCs: carbon shortage, water provisioning, flood control, groundwater recharge, pollution amelioration, recreation
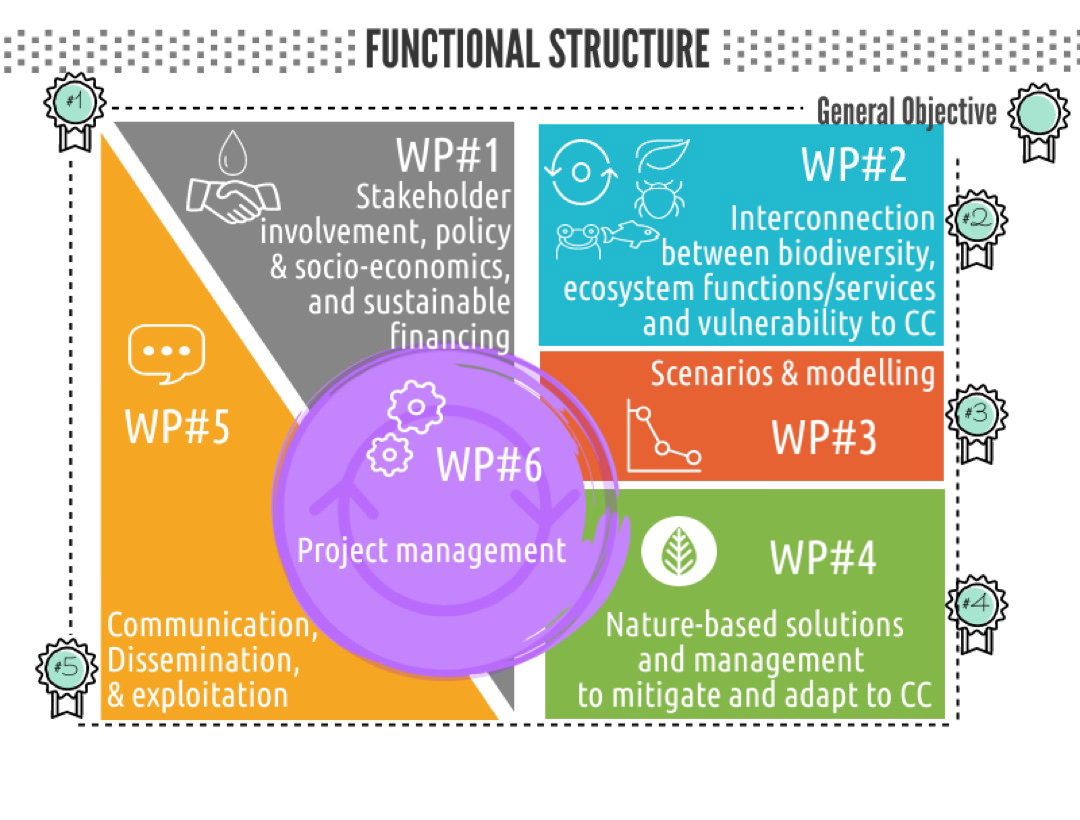
Implementation of ponds and pondscapes as Nature-Based Solutions for climate change mitigation and adaptation, biodiversity conservation and delivery of ecosystem services
Develop a multidimensional framework to support the effective implementation of pondscape NBS for CC mitigation and adaptation, biodiversity conservation and ES/NCP delivery, based on empirical investigation and collaboration with stakeholders
Understand how biodiversity, ecosystem state and processes, and ES/NCP co-vary and interact in pondscapes across a climatic gradient
Use empirical data, incorporating direct and indirect interactions and feedbacks between CC, biodiversity, ES and connectivity, to develop a modelling framework predicting the impact of CC on biodiversity and ES of ponds for various land use and pondscape scenarios
Develop efficient and effective NBS for CC adaptation and mitigation through pondscape management as well as tools and guidance for their implementation
Communication, dissemination and exploitation of the results
between biodiversity, Ecosystem Services and climate in pondscapes at multiple spatial scales
for pondscapes in EU and the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC) in the context of climate change, land use change, and changed policies
effective and multifunctional, to be developed and tested at demonstration sites in EU and CELAC countries
on a sustainable finance and investment for NBS implementation
assessment of the proposed NBS in relation to existing barriers, enabling factors, financing and as economic viability, as well as social perceptions of benefits from pond NBS
to ensure that the scientific knowledge produced on the benefits of using pondscapes as ecosystems delivering multiple services is explicitly considered in decision making from local management to EU policies